Do you know if your website is performing as well as it could be and what is technical SEO?
Are you confident in the technical health of your website?
There are over 3.5 billion Google searches daily. Only 0.78% of these searchers click on results on the second page of Google.
That means if you’re not displaying up on the front page of the SERPs, you aren’t getting traffic.
That’s where SEO arrives in.
Of course, mastering SEO is no easy work.
There are many things to consider, from off-page SEO to on-page SEO, content, copy, and technical SEO.
A truly effective SEO strategy involves all these strategies plus regular optimization to ensure consistent returns.
Think of your site as a book. Just as a book needs a clear table of contents, an easy-to-read layout, and a sturdy binding to ensure it can be easily read and found, your website needs a strong technical SEO foundation to rank well on search engines like Google.
Next, you’ll have a solid understanding of technical SEO, why it’s crucial for your website’s success, and how to optimize your website today.
This article deep dives into what is technical and how you use it to increase organic traffic, display up in search, and improve your overall website experience.
What Is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is an area of SEO that covers optimizations that improve search engine ranking by making your website easier for search engines to crawl. Examples include improving website load time, checking robot.txt files, and making redirects work properly.
Necessary, it’s the process of ensuring your site can be seen, crawled, and ranked by search engines.
Search engines, like Google, give preference sites that meet their webmaster guidelines. The basic principles state your site content should be accurate, easy to access, and user-friendly.
If your website speed loads slowly, has an unresponsive design, or lacks a secure connection, your content will not meet these guidelines. Google uses Core Web Vitas to determine what type of experience users get when they land on your page. These are increasingly important in determining the quality of your page, who impact your page ranking.
What is technical SEO also added to ensure your site is accessible to search engine users and crawlers? If your site has broken links or pages that can’t be found, Google will have a tough time indexing your website. This can result in a lower search ranking.
This is where technical SEO comes in because it can help you improve the technical characteristics of your site to improve organic traffic.
Why is Technical SEO Important?
Imagine you write the most amazing content around the world. It’s content that everyone should read.
People would pay lots of money just to read it. Millions are eagerly waiting for the notification that you’ve posted this fresh, incredible content.
Finally, the day comes, and the notification is sent. Customers excitedly hit the link to read your post.
Then, your web page takes over 10 seconds to load. People are annoyed, and they don’t want to wait.
As a result, for every second it takes for your web page to load, you’re losing readers and increasing your bounce rate.
It doesn’t matter how great that content is — Your website isn’t functioning well, and you’re losing precious traffic.
That’s just one example of why technical SEO is so important.
Without it, Google and other search engines are incapable of seeking, crawling, and indexing your website.
If search engines can’t access your website, you can’t rank, and you become one of the 90.63% of sites that get no organic search traffic from Google. Oh my gosh.
What is technical SEO and the importance following reasons show technical SEO:
1. Improves Website Crawling and Indexing:
Search engines use bots to crawl sites, understanding and indexing their content. Technical SEO optimizes your website’s structure, making it easier for these bots to navigate your website, find pages, and index them appropriately.
Not proper technical SEO, even high-quality content may remain invisible to search engines. Content is king.
2. Enhances User Experience:
Technical SEO directly impacts how users interact with your site. A website that loads quickly, is easy to navigate, and is free from broken links or errors offers a good user experience.
This keeps users on your website longer but signals to search engines that your website is of high quality, which can improve your rankings.
3. Mobile Optimization:
With a majority of internet users accessing the web through phone devices, having a mobile-friendly site is essential.
Technical SEO involves optimizing your website for mobile, ensuring fast loading times, and making sure your website is usable on a small screen. This is important for ranking best, especially since Google uses mobile-first indexing.
4. Website Speed:
Website speed is a ranking factor because search engines aim to provide users with the best possible experience.
Technical SEO techniques, such as leveraging browser caching, minimizing code, and optimizing images significantly improve your website’s loading times.
5. Secure and Accessible Website:
Ensuring your site uses HTTPS is a critical aspect of technical SEO. A secure website protects your users’ information and is favored by search engines.
Additionally, making your site accessible to users with disabilities not only broadens your audience but improves your SEO.
6. Avoids Duplicate Content Issues:
Technical SEO helps prevent duplicate and manage content, which can dilute your website’s relevance and potentially lead to lower rankings.
Using canonical tags and proper redirects, you can tell the search engines which pages are primary and should be indexed.
7. Prepares for Future Technologies:
As search engine algorithms evolve and new technologies emerge, a solid tech SEO foundation helps ensure your website can adapt and continue to great performance.
For example, the growing importance of voice search and AI technologies means sites must be structured in ways that these new technologies can understand and interact.
What is Technical SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is the process of evaluating your site to view how well it is performing on search engines. It can be used to find technical issues that are preventing a site from ranking as high as possible.
SEO technical site audits are a good way to create actionable plans to outperform your competitors, identify opportunities within your site, find and fix points, and better client experiences.
Regularly perform technical SEO audits, on-page SEO audits, and off-page SEO audits.
As you go via your audit, you’ll find places where you can improve or optimize your site performance to improve performance and keep website visitors happy.
While you can’t fix every error at once, you can figure out what’s wrong and devise a plan to fix it.
Main Components of Technical SEO
Let’s dive into the most important aspects of what is technical SEO:
1. Website Speed Optimization
The speed at which your site loads is not just an important part of providing a great user experience; it’s also an important factor in SEO performance.
Importance of Website Speed for SEO
- Search Engine Ranking: Google and other search engines prioritize readers’ experience, in their ranking algorithms. A fast site provides a better experience, making website speed a critical factor in search rankings. Slowly loading websites can suffer lower rankings.
- Conversion Rates and User Experience: Site speed directly impacts how users perceive your website. Faster websites are more likely to retain users, reduce bounce rates, and increase conversion rates. Visitors are less patient than ever, with many expecting a website to load in 3 seconds or less.
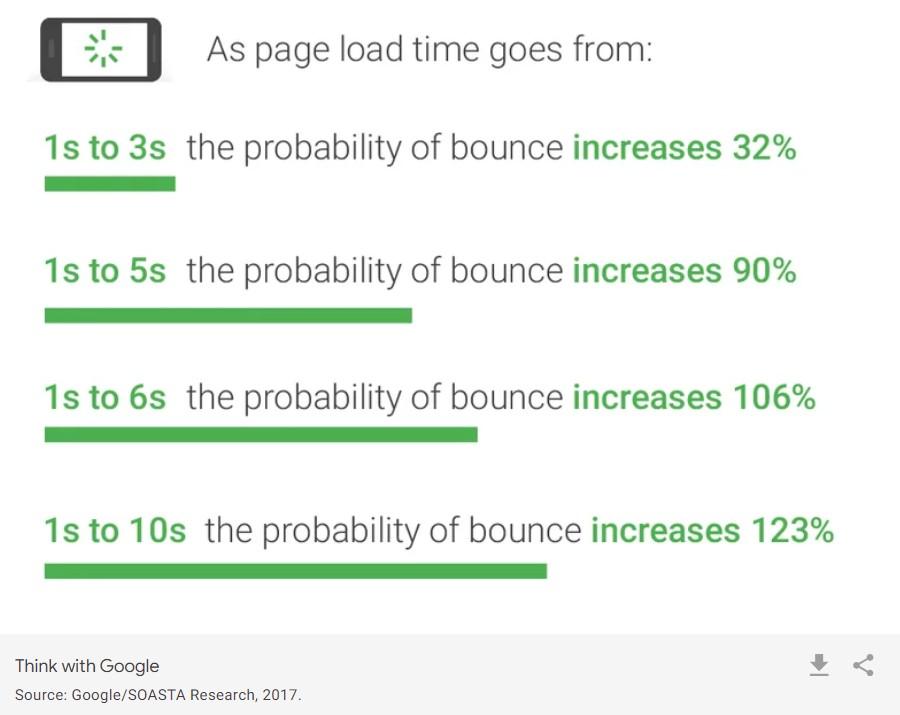
- Phone Experience: With the increasing prevalence of phone browsing, speed becomes even more crucial. Phone users often have faceless stable internet connections, making optimization important for keeping your website accessible to everyone.
Tools for Measuring Site Speed
Several tools can help you analyze your site’s speed and identify areas for improvement:
- Google PageSpeed Insights: This tool provides valuable insights into your site’s performance on mobile and desktop devices. Both a speed score and suggestions for improvement are provided.
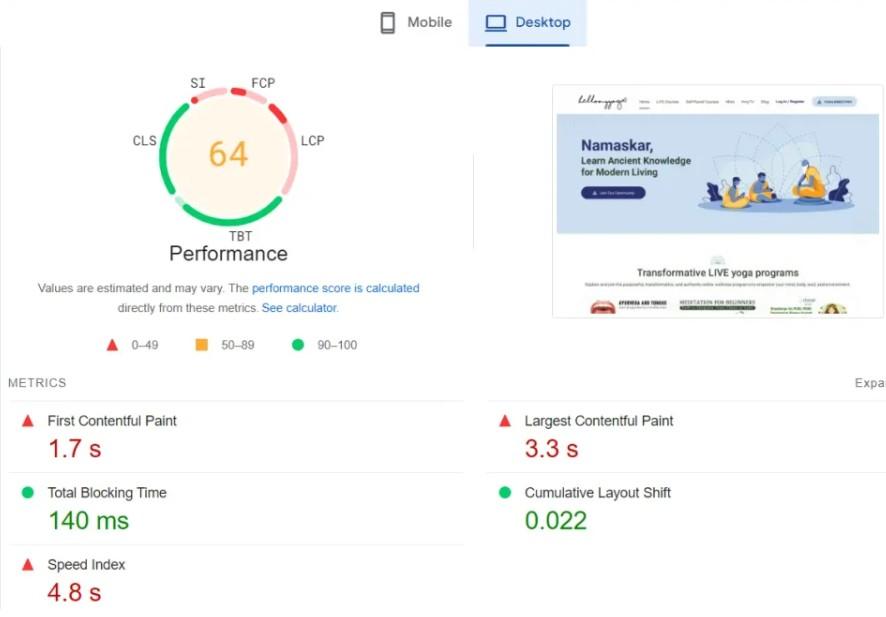
- GTmetrix: GTmetrix analyzes your page’s speed performance using Google PageSpeed and YSlow scores to provide actionable recommendations.
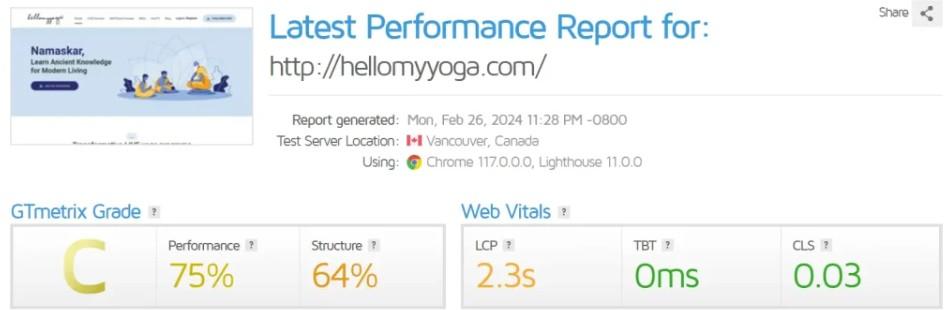
Strategies to Improve Site Loading Times
Improving your site’s loading times adds a mix of quick wins and longer-term strategies:
- Optimizes Images: Large images can significantly display down your pages. Compressing images and using the right formats (like WebP) can reduce their size without sacrificing quality.
- Enable Browser Caching: Browser caching stores parts of your website on a visitor’s device on their first visit, reducing load times on subsequent visits. Use caching for static resources such as JavaScript, CSS, and images.
- Minimize HTTP Requests: less the number of elements (images, scripts, and CSS files) your web page needs to load. Combine files where possible, and use CSS sprites for pictures.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): CDNs distribute your content across various servers worldwide, allowing users to download your website’s files from the closest server, speeding up access.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Removing unnecessary characters from your code (such as whitespace, unused code, and comments) can lessen file size and improve load times.
- Optimize CSS and JavaScript Loading: Use asynchronous loading for JavaScript files and prioritize above-the-fold content to load first, so visitors can start interacting with your website as quickly as possible.
- Improve Server Response Time: Address performance bottlenecks like slow database queries, slow routing, or inadequate memory. If necessary, upgrade your hosting solution.
2. Mobile Friendliness
What is local SEO, In today’s digital world, mobile friendliness is not just a feature—it’s an intensity. With a majority of internet users accessing sites from phone devices, ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is crucial for both user experience and SEO.
Impact of Mobile Responsiveness on SEO
- Google’s Mobile-Fist Indexing: Google predominantly uses the phone version of the content for indexing and ranking. This shift to mobile-first indexing underscores the importance of having a mobile-friendly site for SEO.
- User Engagement and Behavior: Smartphone users expect fast, easy-to-navigate sites on their devices. A website that performs poorly on mobile is likely to have higher bounce rates and lower, engagement negatively affecting its SEO performance.
How to Make a Website Mobile-Friendly?
- Responsive Design: Use a responsive design that automatically adjusts the layout and content according to the device’s screen size. This ensures your website is accessible and navigable on all devices, from mobile and desktops.
- Simplify Navigation: Phone screens offer limited space. Simplify your website’s navigation to make it easy for mobile phone users to find what they looking for with minimal taps or swipes.
- Optimize Images and Media: Compress images and use responsive images that adjust to screen sizes. Reduces load times and data consumption for phone users.
- Use Large, Readable Fonts: Small text is read too hard on phone devices. Make sure your font sizes are large enough to be readable without zooming.
- Avoid Flash: Flash is not supported on most phone devices and can hinder your website’s usability. You can use HTML5 or other web standards for interactive elements or animations.
- Optimize for Touch: Design your website with touch in mind. Ensure buttons and links are easy to click, and consider the ergonomics of touch navigation.
3. SSL Certificate
SSL, which means Secure Sockets Layer, is a technology that encrypts the connection between a user’s browser and the server where a site is hosted.
This encryption ensures that any information exchanged between the user and the website, such as personal details, credit card information, or login credentials, is secure from hackers and remains private.

Importance of SSL for SEO
- Ranking Signal: SSL is a ranking signal confirmed to Google. All else being equal, websites with SSL certificates may rank higher in search engines than those without.
- Increased User Trust: The increased trust that comes with SSL can lead to good user engagement rates, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates, all of which are positive signals to search engines about the quality and reliability of your site.
- Secure Browsing Experience: The search engine’s purpose is to provide users with safe browsing experiences. Websites with SSL certificates contribute to this goal, making them more likely to be liked by search engines.
How to Implement SSL?
- Buy the SSL Certificate: The SSL certificates are provided by Certificate Authorities (CAs). Some web services offer SSL certificates are often included as part of web hosting packages, sometimes even for free.
- Activate the Certificate: After obtaining your SSL certificate, you’ll need to activate it. Its processes vary depending on your hosting provider and usually involve a generated Certificate Signing Request (CSR) on your server.
- Install the Certificate: After activation, you’ll receive your SSL certificate, which you install on your web server. Again, your hosting provider will likely have instructions and may even handle this step for you.
- Update your website to Use HTTPS: Installing your SSL certificate, be sure your site uses HTTPS (the secure version of HTTP) by default. This might include updating settings in your CMS, or web hosting environment, or manually updating links to resources (like stylesheets and images) to use HTTPS.
Read Also: What is Off-Page SEO Techniques? 17 Best Methods
4. Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Structured data markup, often associated with schema markup, is a form of code that you can include in your site’s HTML to help search engines understand the content of your pages well.
This code provides search engines with explicit clues about the meaning of a page and its content, enabling them to show your site in search results more effectively.
Instances — you can tell search engines that a certain piece of text is the name of an event, the author of a post, or the cooking time for a recipe.
Benefits of Structured Data for SEO
- Rich Snippets: Sites with structured data can qualify for rich snippets in search results. These are enhanced search listings, adding visual enhancements such as images, star ratings, or additional information such as cooking times for recipes. Rich snippets can significantly increase your website’s click-through rates.
- Improved Search Engine Understanding: Your content’s context is better understood by search engines when it is structured. This clearer understanding can lead to good indexing and, potentially, a higher ranking for relevant queries.
- Support Voice Search: With the rise of voice search, structured data becomes even more important. Devices such as speakers use structured data to understand and deliver answers to voice queries, making your content more accessible via voice search.
- Increase in Traffic and Engagement: By providing more informative and visually appealing search results, structured data can increase the likelihood of users clicking on your site. This can lead to good user engagement and higher traffic.
Tools for Testing and Implementing Schema Markup
- Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool: This tool allows you to paste in a code snippet or URL to check for proper implementation of structured data. It helps debug and validate your structured data.
- Schema.org: The official website of the schema project provides comprehensive documentation, examples, and vocabulary you can use to mark up your pages correctly.
- Google’s Rich Results Test: This tool tests your page to see if it’s eligible for rich snippets in Google’s search results, providing a preview of how your page might appear.
- Structured Data Markup Helper by Google: This tool helps you visually tag elements on your site without directly editing the HTML. You can choose the data type, point, and click to tag your content. Schema markup will be generated for you by Google.
5. XML Sitemaps
XML Sitemaps are an important tool in the SEO toolkit, serving as a roadmap for search engines to follow when crawling your site. They list the URLs of a website along with additional metadata about each URL, like when it was last updated, how often it changes, and its crucial relative to other URLs.
This information helps search engines crawl your website more intelligently.
Purpose of XML Sitemaps
- Facilitates Faster Discovery: XML sitemaps help search engines quickly seek and index your pages, especially useful for new sites or ones with thousands of pages or complex structures.
- Improves Crawling Efficiency: By highlighting the most crucial pages and those that are updated frequently, sitemaps enable search engines to crawl your website more effectively, focusing their efforts where it matters most.
- Supports Pages Not Easily Discoverable: Pages not well-linked to from other websites or within your website (such as pages accessible via forms or user searches) might not be discovered by search engines. Site maps be sure these pages are also indexed.
- Help in Content Categorization: The metadata provided in sitemaps can help search engines understand the content of your website better, ensuring it’s indexed, and returned in search results where it’s most relevant.
Creating an XML Sitemap:
- Automatic Sitemap Generation: Many content management systems (CMS) such as WordPress, Drupal, and Shopify have plugins or built-in features that automatically generate a sitemap for you. Tools like Rankmath, and Yost SEO for WordPress can create and update your sitemap as your website changes.
- Manual Sitemap Creation: For sites without a CMS or more control, you can manually create an XML sitemap using an XML sitemap generator tool online or by hand-coding it, following the XML sitemap protocol guidelines.
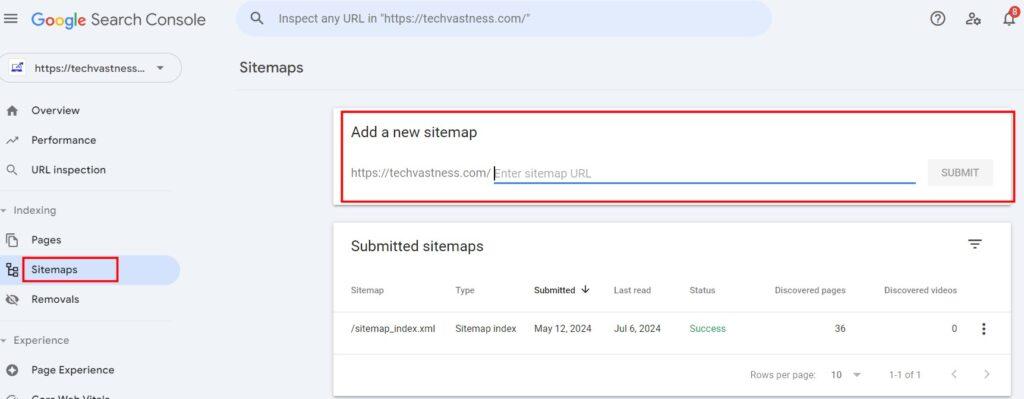
Submitting Your Sitemap to Google:
- Sign in you to Google Seach Console.
- Select your site from the property list.
- Click on the ‘Sitemaps’ under the ‘Indexing’ section.
- Please enter the URL of your sitemap in the ‘Add a new sitemap’ field and click ‘Submit’.
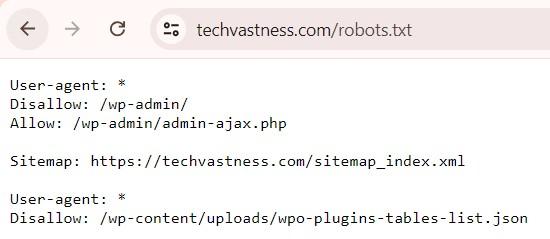
6. Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file is a fundamental part of a website’s SEO strategy, serving as the first line of communication between your website and search engine crawler.
This file, placed in the root directory of your site, tells search engines which pages sections of your website should not be crawled and indexed.
Purpose of Robots.txt
- Controls Crawler Traffic: Robots.txt helps manage the traffic of search engine crawlers on your website, ensuring that significant content is prioritized and unnecessary resources are not wasted on irrelevant or sensitive areas.
- Prevents Indexing of Non-Public Pages: Certain pages on a site, such as admin pages or unpublished content, should not be accessible through search engines. These sections can be prevented from being crawled and indexed by robots.txt.
- Optimizes Crawl Budget: For bigger websites, ensuring search engines spend their crawl budget on top-value pages is important. Robots.txt can help direct crawlers away from low-priority pages, optimizing the use of your website’s crawl budget.
How to Create Robots.txt File?
Start by opening a basic text editor, like Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on Mac. It’s crucial to use a plain text editor to avoid including any formatting in the file.
Write the User-agent and Disallow Rules:
- This User-agent line specifies which crawler the rule applies to. Using User-agent: * applies the rules to all crawlers.
- In the Disallow line, the crawler is told which directories or pages it should not access. Instances, Disallow: /private/ would block access to the /private/ directory.
- If you want to specifically allow certain crawlers to access parts of your website that are generally disallowed, you can use the Allow directive.
- Name the file robots.txt and save it to the root directory or your site. The root directory is the highest folder level that contains your site content (e.g., www.techvastness.com/robots.txt).
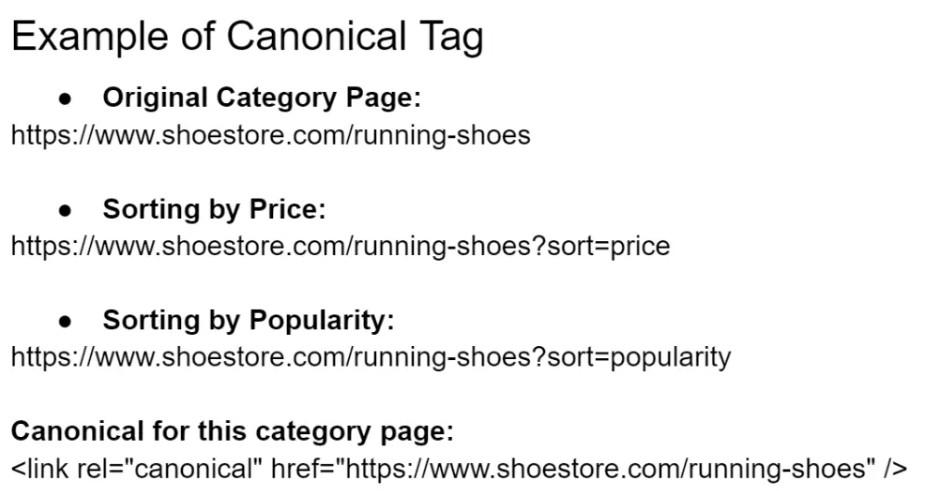
7. Canonical URLs
The canonical URL is the URL of the page that search engines are advised to consider as the authoritative source from several possible duplicates. By specifying a canonical URL, you essentially tell search engines:
“of all the pages with similar content, the most useful is this one. Please it prioritize in search results.”
How to Use Canonical Tag to Prevent Duplicate Content Issues?
- Identify Duplicate Content: First, identify pages on your website that have similar or identical content. This could be product pages with URLs that differ only by a parameter, posts accessible via various paths, or print versions of web pages.
- Deciding on the Preferred URL: Select which version of the URL you want search engines to index and rank. This should be the version that’s most valuable for readers and has the potential to rank top in SERPs.
- Implementing the Canonical Tag: Include a tag in the section of the HTML of the duplicate pages, pointing to the preferred URL.
Instances, if www.example.com/page1 and www.example.com/page1?parameter are duplicates, and you’ve selected www.example.com/page1 as the canonical version, you would include the following tag to the of both pages:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/page1″ />
- Consistency Is Key: Make sure that internal links on your website point to the URL version you’ve designated as canonical. A consistent help of the content reinforces to search engines which version is preferred.
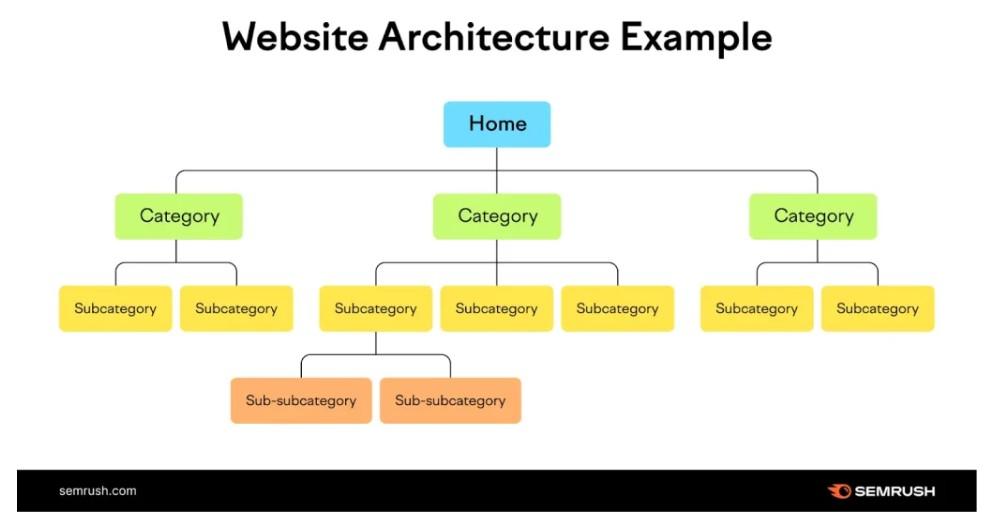
8. Website Architecture and Navigation
A well-structured site architecture and intuitive navigation are not just about aesthetics or readers’ experience; they play an important role in SEO. Search engines crawl sites by following links, internal and external, to understand and index the content of every page.
A coherent website structure and clear navigation paths make it easy for search engines to do their job and for readers to seek the information they need.
Importance of a Well-Structured Site for SEO
- Improve Crawling and Indexing: A logical structure with clear internal linking be sure search engines can easily crawl all of your pages. This via understanding helps in better indexing your content in search results.
- Enhanced User Experience: Users should seek what they want with minimal effort. A well-organized website keeps users engaged longer, reducing bounce rates and increasing the likelihood of conversions, which are positive signals to search engines.
- Efficient Distribution of PageRank: Google’s PageRank is distributed via links. A well-planned architecture be sure that link equity is efficiently passed via your website, boosting the ranking potential of crucial pages.
- Facilitates Content Discoverability: By categorizing content logically, visitors and search engines can discover your site’s breadth of content more easily, enhancing visibility across a wider array of search queries.
Tips for Optimizing Website Architecture and Navigation
Start with a Hierarchy: Before designing your site, plan out its structure. Create a hierarchy that logically categorizes your content into main categories and subcategories. Each core category should be accessible from the homepage and reflect a main area of your business or website content.
- Implement a Simple, Scalable URL Structure: Your URLs should follow your hierarchy, be readable by humans, and logically arrange for search engines. Instances, www.example.com/category/subcategory/page indicate the page’s position within the website hierarchy.
- Use Descriptive Navigation Labels: Navigation menus are a key feature of your website architecture. Label your navigation links with descriptive, keyword-relevant descriptions. This not only helps visitors but also gives search engines context about linked pages.
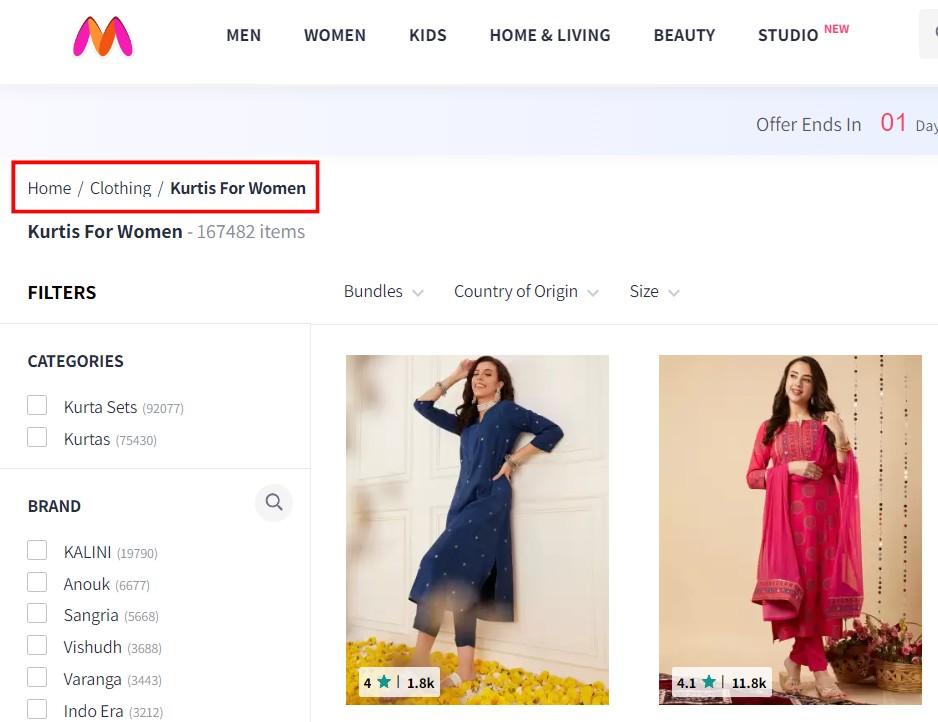
- Use Breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs are navigational aids that display users their current location within a website’s hierarchy. They help visitors navigate your website more effectively and provide search engines with another layer of information about your website structure.
- Optimize Internal Linking: Use internal links wisely to connect your content and guide users and search engines to related topics and crucial pages. Internal links should have descriptive anchor text and be relevant to the target page.
- Minimize Click Depth: Crucial pages should be accessible within three clicks from the homepage. In a shallow website structure be sure that no content is buried too deep for users or search engines to easily find.
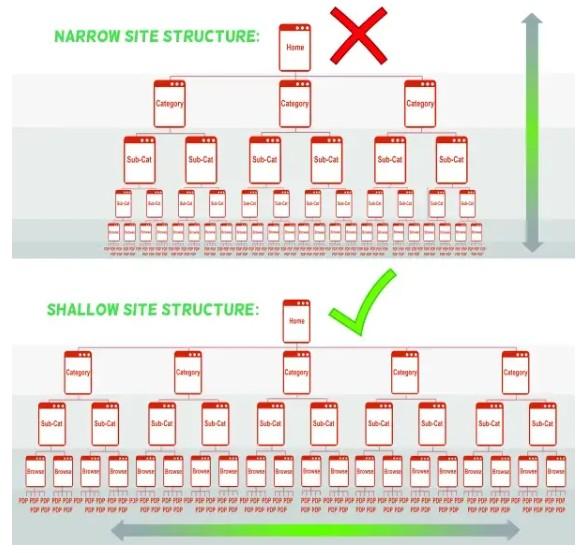
- Use a Sitemap: While primarily for search engines, a sitemap also aids in organizing and planning your website structure. An XML sitemap helps search engines crawl your website, while an HTML sitemap can assist users in navigation.
9. Crawl Errors and Site Health
Crawl errors occur when search engine bots try to access specific pages on your site but fail due to multiple reasons. These errors hinder your site’s ability to be indexed effectively, impacting its visibility in search results.
Regularly monitoring site health and addressing crawl errors is important for maintaining and improving your website’s SEO performance.
How do Identifying and Fix Crawl Errors?
Use Search Console Tools to identify crawl errors. Page Indexing reports, you can view why pages aren’t indexed.
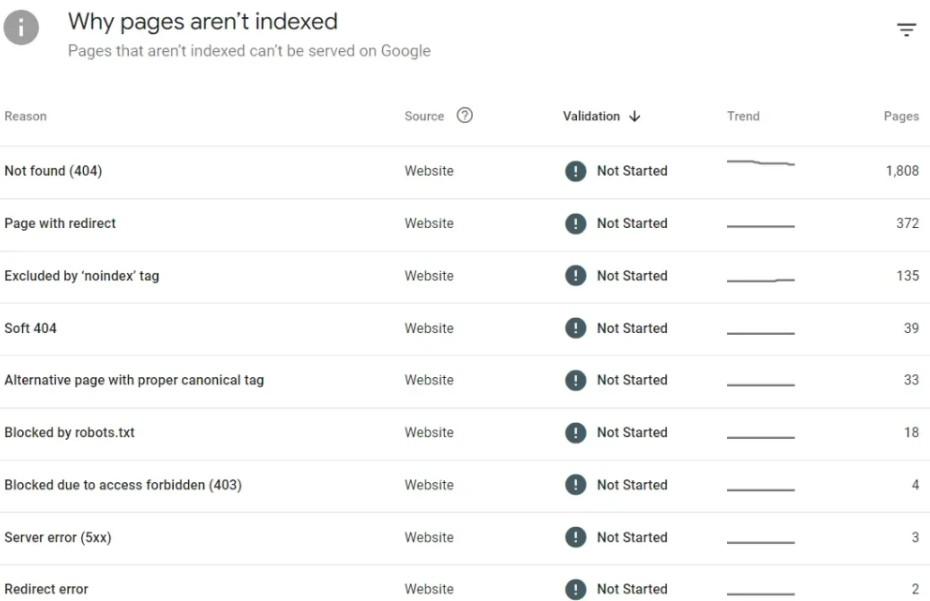
The most common errors that impact your site’s indexing are:
- Server Errors (5xx): This indicates a problem with your server. Check your server’s configuration, and security settings, and be sure it’s not overloaded.
- 404 Errors (Not Found): This occurs when a page doesn’t exist. For removed content, consider implementing 301 redirects to relevant pages or improving your 404 page to help users seek what they’re looking for.
Correct the Errors:
Fix the Broken Links: Use tools to seek and fix broken internal and external links.
- Update Your Sitemap: Be sure your XML sitemap is up-to-date and doesn’t contain URLs that result in errors.
- Improve Server Performance: If server errors are frequent, upgrade your hosting plan and optimize your web server setting, or consult with a server administrator.
- Submit for Reindexing: After fixing the errors, use Google Search Console to request a re-crawl of your website. This prompts search engines to update their indexing based on the corrected pages.
Monitor the health and indexing status of your website with these tools
- Google Search Console
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Ahrefs
- SEMrush
- Moz Pro
10. Core Web Vitals and User Experiences
Core Web Vitals are the set of specific factors that Google considers crucial in a webpage’s overall user experience. They are part of Google’s “Page Experience” signals, which play an important role in search engine rankings.
Understanding Core Web Vitals and their impact on user experience is essential for any SEO strategy, as they directly influence a website’s visibility and performance in search results.
Core Web Vitals consist of 3 primary metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures load performance. To provide a great user experience, LCP should occur within 2.5 seconds of when the page first starts loading.

- First Input Delay (FID): Measures the interactivity. Pages should have an FID of 100 milliseconds or less to be sure of responsiveness.

- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures the visual stability. To be sure a page is stable as it loads, the CLS should be less than 0.1.
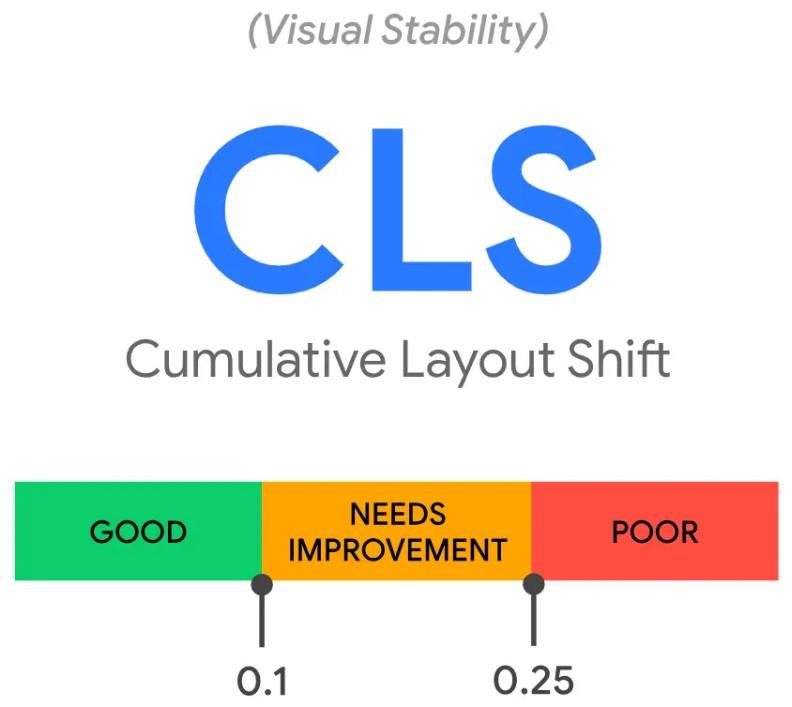
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): It is a fresh concept that replaces FID in March 2024. INP measures a page’s overall responsiveness to user interaction. It observes the latency of taps, clicks, and keyboard interactions throughout a session.
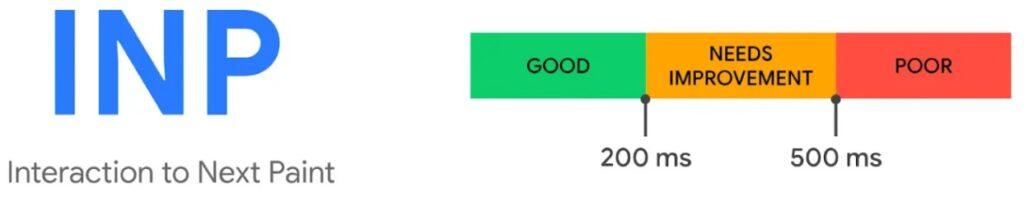
You can look at the Core Web Vitals report in Google Search Console under the Experience section:
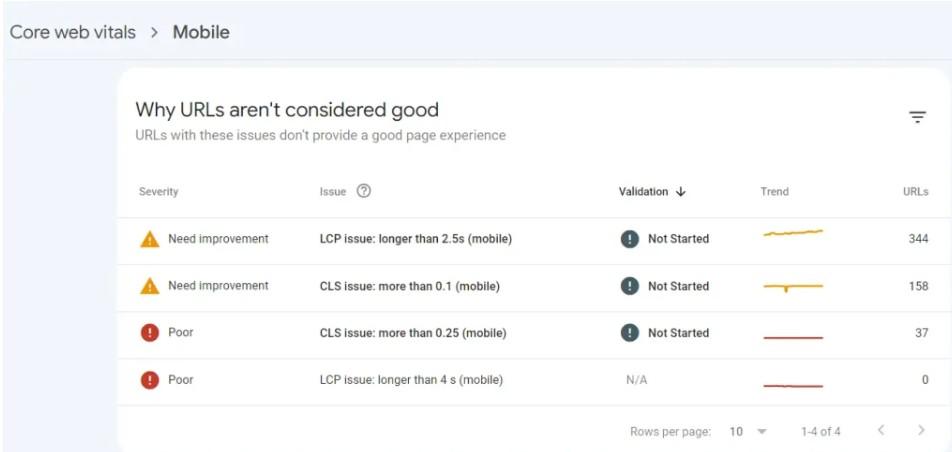
How to User Experience Impacts SEO?
Websites that offer a superior user experience are more likely to rank top in search results. This is because search engines aim to provide users with the greatest possible result, prioritizing sites that meet or exceed these user experience benchmarks.
Read Also: What is Local SEO Optimization? Improve Your Local Rankings!
11. The International SEO and Localization
Internal SEO and localization are about optimizing your site so that search engines can easily identify which country you’re targeting and which languages you use for business.
This process adds strategic planning and implementation of practices such as using hreflang tags for multilingual sites and adhering to good practices for international SEO.
Through these efforts, your content reaches the right audience in the right language, enhancing user experience and potentially increasing global traffic and conversions.
Understanding Hreflang Tags for Multilingual Sites
Hreflang tags are a necessary part of international SEO. They tell search engines which language you using on a specific page, and the search engines can serve that result to users searching in that language.
This is particularly crucial for sites that have content in various languages or similar content targeted at different regions.
A) Implementation:
The Hreflang attribute is included in the element in the HTML document’s head section or HTTP header, specifying the language (in ISO 639-1 format) and the region (in ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 format).
Instances, en-gb for English speakers in Great Britain and en-us for English speakers in the United States.
B) Use Cases:
It’s used for sites that have content in various languages or regional variations of the same language, addressing differences in spelling, currency, and cultural nuances.
C) Benefits:
Proper use of hreflang tags can lessen the likelihood of duplicate content issues, improve targeting in SERPs, and enhance the user experience by directing them to the version of your website most relevant to their language or region.
The Best Practices for International SEO
What is technical SEO best practice for international SEO?
- Site Structure: Select the right URL structure for your international websites. Options are added using country-code high-level domains (ccTLDs), subdomains with gTLDs, or subdirectories with g TLDs. The like depends on your resources, target markets, and SEO goals.
- Localize Content: Beyond the direct translation adapt your content to reflect local cultural nuances, currency, and user behavior. Surely, content resonates with the targeted audience, improving engagement and conversion rates.
- Optimize for Local Search Engines: While Google dominates many countries, don’t ignore local search engines such as Baidu in China, Yandex in Russia, or Nave in South Korea. These search engines have specific requirements that must be understood and optimized for.
- Link Building: You can develop localized link-building strategies. Acquire links from country-specific sites to increase the relevance of your localized content in the eyes of search engines.
- Local User Experience: Consider local norms and preferences in design, customer service, and payment methods. Be sure the site loads quickly in target regions, possibly using a content delivery network (CDN).
- Monitor Performance and Iterate: Use tools such as Google Analytics and Search Console to monitor the performance of your international websites. View metrics such as traffic, bounce rate, and conversion rate by country and language to identify areas for improvement.
What are Advanced Technical SEO Strategies?
Now that you about the primary factor what is technical SEO? let’s learn some advanced strategies:
1. AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the speed and performance of your site on mobile devices are important for retaining users and improving search engine rankings. It is where Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) come into play.

AMP is an open-source initiative aimed at making the web great for all by enabling web pages to load instantly on mobile phone devices.
It is a framework developed by Google in collaboration with other technology publishers and companies. ConThis open-source initiative enables web pages to load instantly on mobile devices, making the web a great place for all. It consists of three main components: AMP HTML, AMP JavaScript (JS), and AMP Cache.
Together, these components allow for the creation of lightweight web pages that load closely instantaneously on phone devices. AMP achieves this by easing HTML code, prioritizing resource loading, and utilizing a content delivery network (CDN) to cache and serve optimized pages.
- The Benefits of Implementing AMP
- Improve Page Load Speed
- Increased Phone Traffic
- Great Search Engine Ranking
- Enhanced Users Experiences
- Increase Visibility in Google Search
2. Using CDN (Content Delivery Network)
A CDN is a network of servers distributed globally, designed to deliver web pages and content to visitors based on their geographic location.
By caching content on various servers world, a CDN ensures that when a user requests your web page, the content is delivered from the closest server, thereby less latency, improving website speed, and enhancing the user experience.
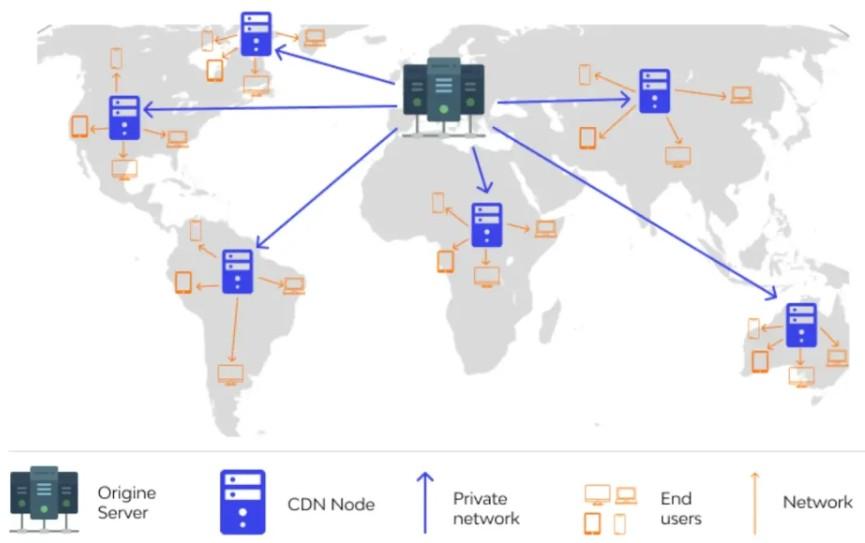
Benefits of Using the CDN for SEO
- Improved Page Load Time: Serving content from the closest geographical server to the users, CDN drastically less page load time. This is important for SEO as faster sites tend to rank top in search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Lessed Server Load: CDNs handle the bulk of traffic and bandwidth demand by caching content across their network, less the load on your primary server. This prevents your website from crashing during traffic spikes, ensuring it remains accessible and performs great at all times.
- Enhanced User Experience: Fast-loading pages and regular uptime contribute to a good user experience, the key factor in SEO rankings. The happy users are likely to stay longer, explore more pages, and return to a fast-performing website.
- Increased Content Redundancy and Availability: With content replicated across various servers, a CDN be sure that your site remains available even if one or more servers go down. This redundancy can protect your website’s SEO performance by minimizing downtime.
3. SEO Consideration for Single-Page Applications (SPAs)
Single-page applications (SPAs) have gained increasing popularity due to their ability to provide a seamless and dynamic user experience, similar to desktop applications. SPAs load a single HTML page and dynamically update content as the users interact with the app, without reloading the page.
While SPAs can offer crucial performance and user experience benefits, they also present a unique challenge for search engine optimization (SEO).
A) Make Sure Content is Crawlable and Indexable
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Pre-render pages on the server using SSR. This ensures that search engines can crawl and index your content effectively because they receive fully rendered HTML for every page.
- Pre-Rendering: Consider pre-rendering your SPA pages into static HTML if SSR is not feasible. Tools and services such as Prerender.io can generate and serve static versions of your pages to search engines, ensuring content is accessible.
- Dynamic Rendering: Alternative to SSR and pre-rendering, dynamic rendering serves a client-side version of the SPA to users and a pre-rendered version to search engines. These approaches can balance user experience with SEO needs.
B) Enhance Navigation and Linking
- Use HTML5 History API: For the SPAs, the HTML5 History API allows you to update the browser’s history and URL without a full page reload. This is important for creating navigable, bookmarkable URLs for different looks within your SPA.
- Internal Linking: Make sure that your SPA involves proper internal linking. This helps search engines discover content and understand the website structure, improving your website’s SEO.
C) Improve Page Load Performance
- Optimize Assets: Minimize JavaScript and CSS files, and compress the image. Efficient asset management lessens load times, improving user experience and SEO.
- Lazy Loading: Implement lazy loading for pictures and non-critical resources. This means only loading assets when needed, which can significantly improve page load times.
D) Structure Data and Metadata
- Dynamic Metadate: Use JavaScript to dynamically update metadata (title tags, descriptions) when the content is improved. This helps search engines understand every “page” within your SPA.
- Structured Data: Use structured data (schema markup) to help search engines understand the content and context of your page. This is particularly crucial for SPAs, where content relationships might not be as obvious as in multi-page applications.
E) Monitor and Testing
- Google Search Console: Use the Google Search Console tool to monitor how great your SPA is crawling and indexing. The tool also helps identify any crawled issues or errors that need to be addressed.
- SEO-Friendly URLs: Make sure that your SPA uses SEO-friendly URLs. Avoid hashbangs(#!) if possible, because they are not recommended for SEO. Instead, Implement clean, readable URLs that reflect the content of a page.
What is Technical SEO Ranking Factors?
- Mobile-Friendly: Sites optimized for phone devices rank better, especially since Google mobile-first indexing.
- Page Speeds: Fast-loading pages are favored by search engines, providing a good user experience.
- Secure Site (HTTPS): Secure websites using HTTPS are given preference over non-secure websites.
- Core Web Vitals: Google’s user experience metrics (loading, visual stability, and interactivity) are ranking factors.
- Structured Data Markup: Using schema.org helps search engines understand the content and can enhance visibility in search results.
- User Experience (UX): A great user experience, adding easy navigation and engaging content, indirectly affects rankings.
- Crawlability: Search engines must be able to crawl and index a website’s content; proper use of robots.txt and sitemaps facility this.
- Site Architecture: A logical structure with a clear hierarchy enhances indexing and user experience.
- Internal Linking: Proper use of internal linking helps distribute page authority throughout the website and improves navigation.
- Mobile Page Speeds: Specily, the loading speed of your website on mobile devices can impact rankings, particularly after mobile-first indexing.
- URL Structure: Clear and descriptive URLs are easy for search engines to understand and can contribute to good rankings.
- Server Location: The geographical location of your server can influence website speed and, indirectly, SEO rankings for regional searches.
- 404 Errors: Too many 404 errors can be harmful to user experience and potentially affect a website’s ranking.
- Canonical Tags: The use of canonical tags helps prevent issues with duplicate content across various URLs.
- Robots Meta Tags: Controlling crawler access and indexation of specific pages can affect which content is ranked.
- Hreflang Tags: Multilingual or multi-regional websites, hreflang tags help search engines serve the right language or regional URL in search results.
Read Also: What is SEO in Digital Marketing? Your Step-by-Step Explained!
What is the Technical SEO Checklist
- Make sure the website is using HTTPS
- Implement responsive design for mobile-friendly
- Optimize website speed
- Use a Content Delivery Network for global content delivery
- Create and submit an XML sitemap to a search engine
- Configure robots.txt to control the crawler access
- Fix crawl errors and broken link
- Use hreflang tags for multilingual or multi-regional websites
- Use structures data markup for rich snippets
- Optimize URL structure for clarity and keyword add
- Make sure the internal linking structure
- Identify and fix technical SEO issues on your website regularly
- Controlling and improving Wore Web Vitals scores (LCP, INP, CLS)
- Make sure accessibility for users and search engine crawlers
- Secure the site against hacking and spam
- Optimizing pagination and faceted navigation
- Avoid duplicate content issues with the canonical URLs
- Make sure 404 pages are user-friendly and add a search function or link to the homepage
- Minimize the use of JavaScript for important content and links
- Ensure compliance with web standards by validating HTML and CSS
- Regular update CMS and plugins to the latest versions for security and performance
- Monitor website performance and user experience across different devices and browser
- Secure data transfers with SSL certificates
- Implement AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) for key phone content (optional)
- Leverage lazy loading for pictures and non0critical resources
- Optimizing server response time and configuring server settings for optimal performance
What is Technical SEO Tools?
1. Google Search Console

Monitors site performance in Google search results, identifies crawl errors checks mobile usability, and examines baclinks.
2. Screaming Frog SEO Spider

Crawls sites to identify technical issues, like broken links, duplicate content, missing meta tags, and redirects.
3. PageSpeed Insights (Google)

Analyzes the content of a web page, then generates suggestions to build that page faster, measuring mobile and desktop performance.
4. Ahrefs

Offers website audit features to detect technical SEO issues, backlink analysis, keyword research, and competitor analysis.
5. SEMrush

Provides a comprehensive toolkit adding website audits, keyword research, tracking SEO performance, and competitor analysis.
6. Moz Pro

Offers website crawling to identify SEO issues, keyword research tools, and insights on-page optimization and link-building opportunities.
7. GTmetrix

Analyzes the loading speeds of web pages, provides performance scores, and offers actionable recommendations to improve site speeds.
8. Yoast SEO (for WordPress)

Focus on making site content SEO-friendly, generate XML sitemaps, and help with content analysis and readability.
9. Google Structured Data Testing Tool
Checks for schema markup errors on a web page to validate structured data.
10. DeepCrawl
Provides deep website crawling and analysis to understand and monitor technical issues, website architecture, and SEO performance over time.
What is Technical SEO’s Future?
The future of technical SEO is evolving rapidly, shaped by technological advancements, improved search engine algorithms, user behavior trends, and the increasing crucial of user experience.
As we view ahead, several key trends are set to influence tech SEO, making it more integral to online success than ever.
1. AI and Machine Learninig
Search engines are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to understand user intent, personalize search results, and improve the accuracy of their rankings.
This means technical SEO will need to adapt to this technology by focusing on content quality, user engagement, and relevance, beyond traditional optimization techniques.
2. Voice Search Optimization
Voice search is becoming more common with the rise of virtual assistants and smart speakers. This shift requires a fresh approach to technical SEO, emphasizing natural language processing, local SEO, and conventional queries, because voice searches are often more localized and spoken in natural, conversational language.
3. Mobile-First Indexing
As phone usage continues to outpace desktop, mobile-first indexing is now the standard for Google. This shift emphasizes the significance of mobile-friendly design, fast loading time, and responsive web design.
Technical SEO strategies must prioritize the phone user experience, ensuring sites are optimized for speed, navigation, and content accessibility on smaller screens.
4. Core Web Vitals and User Experience
Google’s introduction of Core Web Vitals as ranking factors highlights the significance of user experience metrics in SEO. This involves loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability to pages.
What is technical SEO’s future efforts will need to focus on optimizing these aspects to ensure a smooth, fast, and engaging user experience, directly impacting search rankings.
5. Structured Data and Schema Markup
As search engines aim to provide rich results and direct answers within SERPs, the role of structured data and schema markup becomes increasingly significant.
Implementing this markup helps search engines understand the content and context of web pages, facilitating the show of rich snippets and enhancing visibility in search results.
6. Security and Privacy
With growing concerns over data security and privacy, HTTPS has become a standard, and its significance will grow. Technical SEO strategies will need to incorporate robust security measures, adding secure protocols, privacy practices, and data protection, to meet search engine requirements and user expectations.
7. Emerging Technologies
The integration of emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and the Internet of Things (IoT) into search and user experiences will open fresh for technical SEO.
Optimizing for this technology will require innovative approaches to content, metadata, and user engagement strategy.
FAQs
1. What is a technical SEO audit?
The technical SEO audit is a comprehensive examination of a site to identify issues affecting its search engine visibility. It covers aspects such as website speed, mobile-friendliness, indexation, structured data, security, and more. The goal is to seek and fix problems that could hinder the website’s performance in search results.
2. What is technical SEO in digital marketing?
Technical SEO is a process of optimizing a site’s infrastructure to help search engines crawl and index it more effectively. It includes improving website speed, making sure of mobile-friendliness, implementing SSL for security, optimizing robots.txt, XML sitemaps, and more. It’s an important part of digital marketing because it lays the foundation for a site’s visibility and ranking in search engine results.
3. What am I looking for in a technical SEO audit?
When you’re performing a technical SEO audit, you should be looking for any issues that could be hindering your site’s ranking in search engines. This involves things that would hinder your website’s speed performance, duplicate content, and security issues.
4. How to do a technical SEO audit?
Perform a technical SEO audit, you should:
Analyze the site’s crawl ability and indexation status using tools such as Google Search Console.
Check the website’s mobile-friendliness and loading speeds with tools such as Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and PageSpeed Insights.
Review security aspects, ensuring the website uses HTTPS.
Inspect on-site SEO factors such as structure data, XML sitemaps, and robots.txt files.
Any duplicate content or canonicalization issues identified and resolved.
Evaluate the site’s architecture for user and search engine friendliness.
5. What are the benefits of technical SEO?
increased crawlability and indexation by search engines, enhanced security, and ultimately, top rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs). This leads to more visibility, traffic, and potential conversions.
What is Technical SEO? Final Thoughts
There are three different aspects of SEO and technical SEO is the most crucial of the three.
If your technical SEO fails, it won’t matter how amazing your on-page SEO is.
It also won’t matter how good you are at off-page SEO if you’re horrible at the technical stuff.
Don’t let the idea of it being “technical” or complex overwhelm you. You start with the large, critical aspects discussed above and tackle them one problem at a time.
You keep this checklist in mind to get started:
- Crawl your site
- Manually search Google
- Ensuring only one version of your website is browseable
- Conduct the on-page SEO checks
- Manage your external and internal links
- Check your website seed
- Leverage your analytics and compare website metrics
- View for any security issues
- Check your off-site SEO and perform backlinks audits

